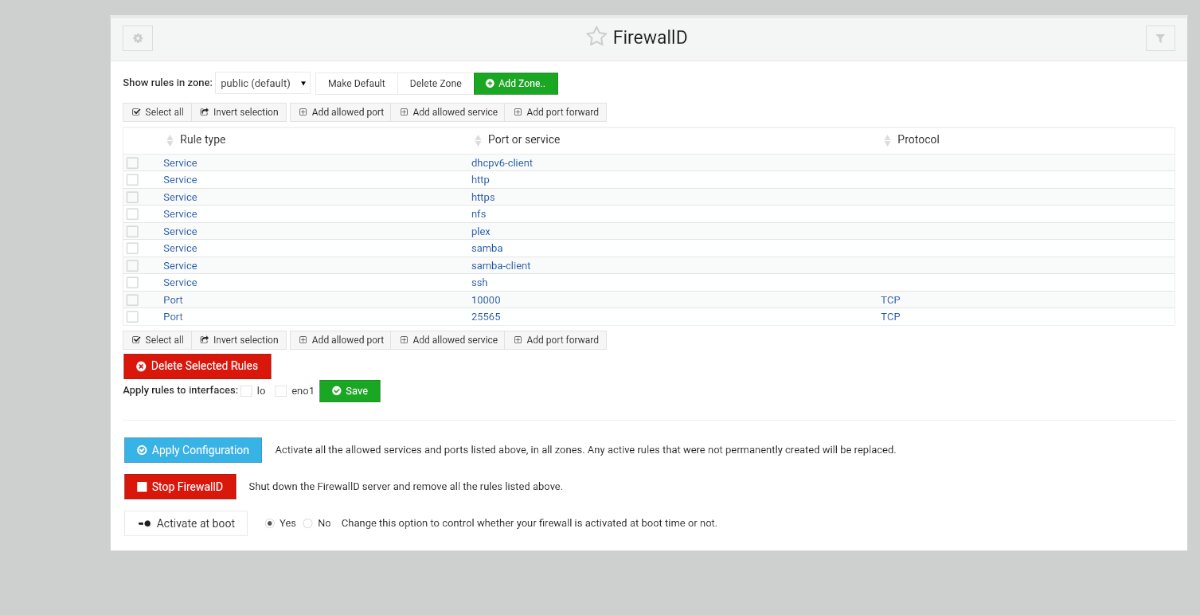
FirewallD is a complex firewall system for Linux operating systems. It ships by default on Fedora and many other Linux OSes, and for a good reason. It is powerful, highly configurable, and secure. But it isn’t great to set up by hand.
If you don’t want to fuss around and want to get FirewallD up and running on your Ubuntu Server system so you can get on with your work, this guide is for you. Follow along as we show you how to set up FirewallD on Ubuntu Server the easy way!
Getting Webmin installed on Ubuntu Server
If you want to use the built-in FirewallD module inside of Webmin on your Ubuntu Server, you’ll have to install the Webmin app. Thankfully, Webmin supports the Ubuntu platform well.
To start Webmin installation on Ubuntu Server, launch a terminal window and log into the machine over SSH. Or sit at the server physically. Then, when you’ve got access to the Ubuntu Server terminal, enter the commands below to get Webmin working.
wget http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/webadmin/webmin_1.981_all.deb
sudo apt install ./webmin_1.981_all.deb
Setting up Webmin on Ubuntu Server is pretty straightforward. However, if you need more guidance on how to get this program working on your system, we’ve got you covered. Follow our guide on how to set up Webmin on Ubuntu Server.
Setting your root password
Using the Webmin web UI on Ubuntu Server requires access to the root password. However, Ubuntu shuts off the root account by default. Therefore, you must set up the password on the root account to gain access to it.
To set up the password on the root account, use the sudo -s command to access root. This command grants you root indirectly.
sudo -s
With root level access gained, it is time to change the password. Using the passwd command, inform Ubuntu that the root password is to be changed. For best results, ensure the root password is memorable and secure.
Note: if you need help generating a password, check out StrongPasswordGenerator.
passwd
Now that your Ubuntu Server’s root account is set up correctly, you’ll be able to log into the Webmin web UI. To access the web UI, open up a new tab in your favorite web browser and visit the link below.
http://YOUR_UBUNTU_SERVER_IP_ADDRESS_OR_HOSTNAME:10000
Installing the “firewalld” package on Ubuntu Server
Webmin cannot interact with FirewallD on your Ubuntu Server system unless the “firewalld” package is installed. Sadly, unlike a lot of other Webmin modules, Webmin can’t install the package automatically. You must do it yourself.
To install the “firewalld” package in Webmin, follow the step-by-step instructions below.
Step 1: Log into the Webmin user interface using “root” as the username and the password you set as the password.
Step 2: Find the menu in the left-hand sidebar and click on it with the mouse.
Step 3: Click on the terminal icon in the sidebar at the bottom. This button will launch a terminal window right inside of your browser with root access.
Step 4: Install the “firewalld” package on your Ubuntu Server using the apt install command.
apt install firewalld -y
Step 5: After installing the “firewalld” package on your Ubuntu Server, you will need to unblock port 10000 over TCP, as your new firewall will lock you out of the Webmin UI.
To unblock, return to the SSH terminal you used to install Webmin and enter the two commands below.
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10000/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reload
When the firewall is updated, press F5 in the browser to refresh Webmin. Then, click on the “Refresh Modules” button at the bottom of the sidebar.
Configuring FirewallD in Webmin
Access the “Networking” section of Webmin in the sidebar. Then, click on the “Linux Firewall” button and follow the step-by-step instructions below.
Adding ports
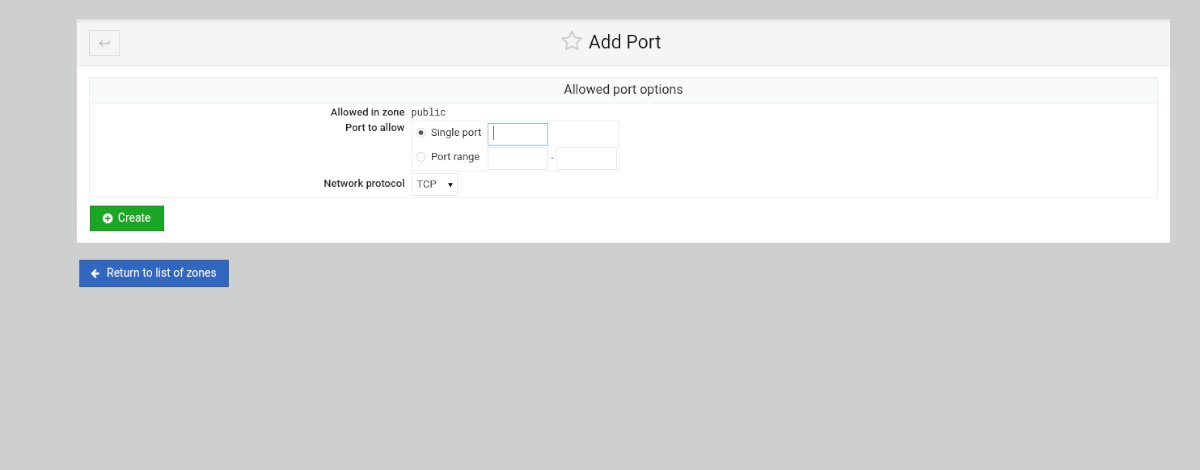
Step 1: In the FirewallD section, find the “Add allowed port..” button and click on it with the mouse to add a new port to the firewall.
Step 2: After clicking on the “Add allowed port” button, FirewallD will open up the “Allowed port options” window. From here, find “Single port” and enter the single port into the box. Or, if it is a range of ports, enter the range in the “Port range” section.
Step 3: Once you’ve entered the port details, find the “Network protocol” section and set it to either TCP or UDP.
Step 4: Find the green “Create” button and select it to add it to your list of rules.
Adding service
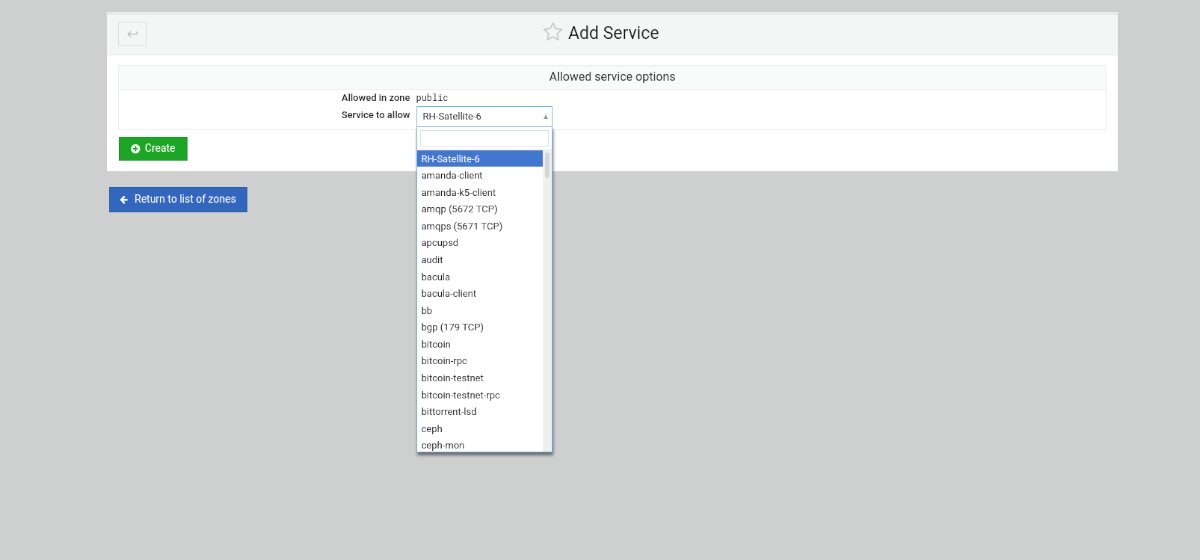
Step 1: Select the “Add allowed service” button to open up the allowed service menu.
Step 2: Find the “Service to allow” area, and click on it with the mouse. Then, type in the search box the name of the service you wish to allow through the Firewall.
Step 3: Select the green “Create” button to add your new service to the FirewallD rules.
Adding port forward
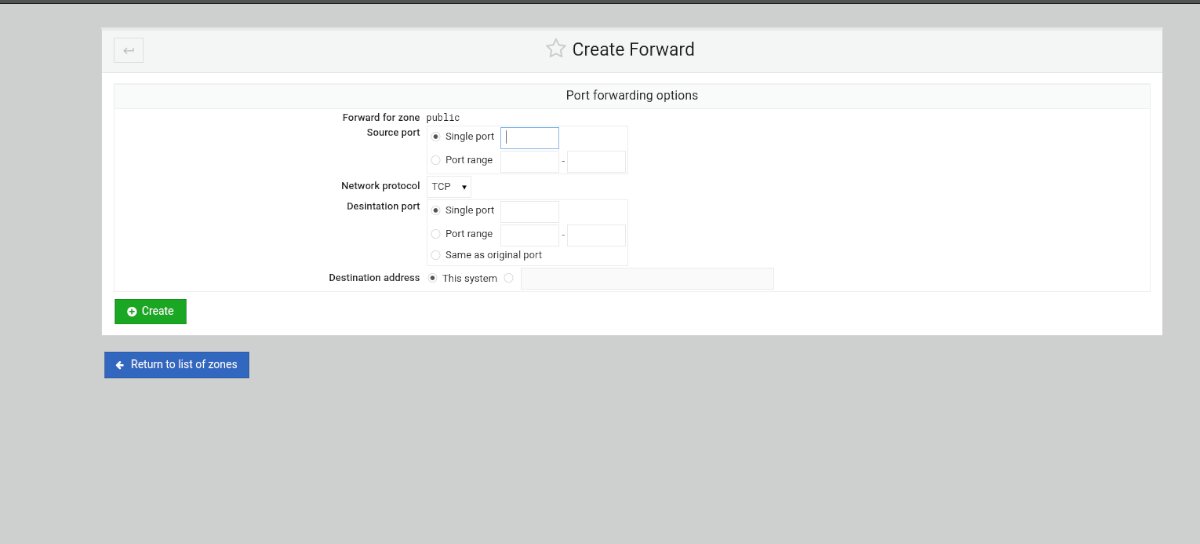
Step 1: Select the “Add port forward” button inside of the FirewallD rules area.
Step 2: Find the “Single port” box and enter the port you wish to forward. Or, select the “Port range” box to add a range of ports.
Step 3: Find the “Destination port” and enter either a single port or a port range.
Step 4: Select the “Create” button to add the rules to the firewall.





