Google’s Messages app has improved exponentially in features. In fact, it’s well on its way to competing with Apple’s iMessage.
The Messages app has specials ‘Chat’ features which, when enabled, add additional features to it such as a typing indicator and read receipts. These features have to be enabled and they work with your phone number.
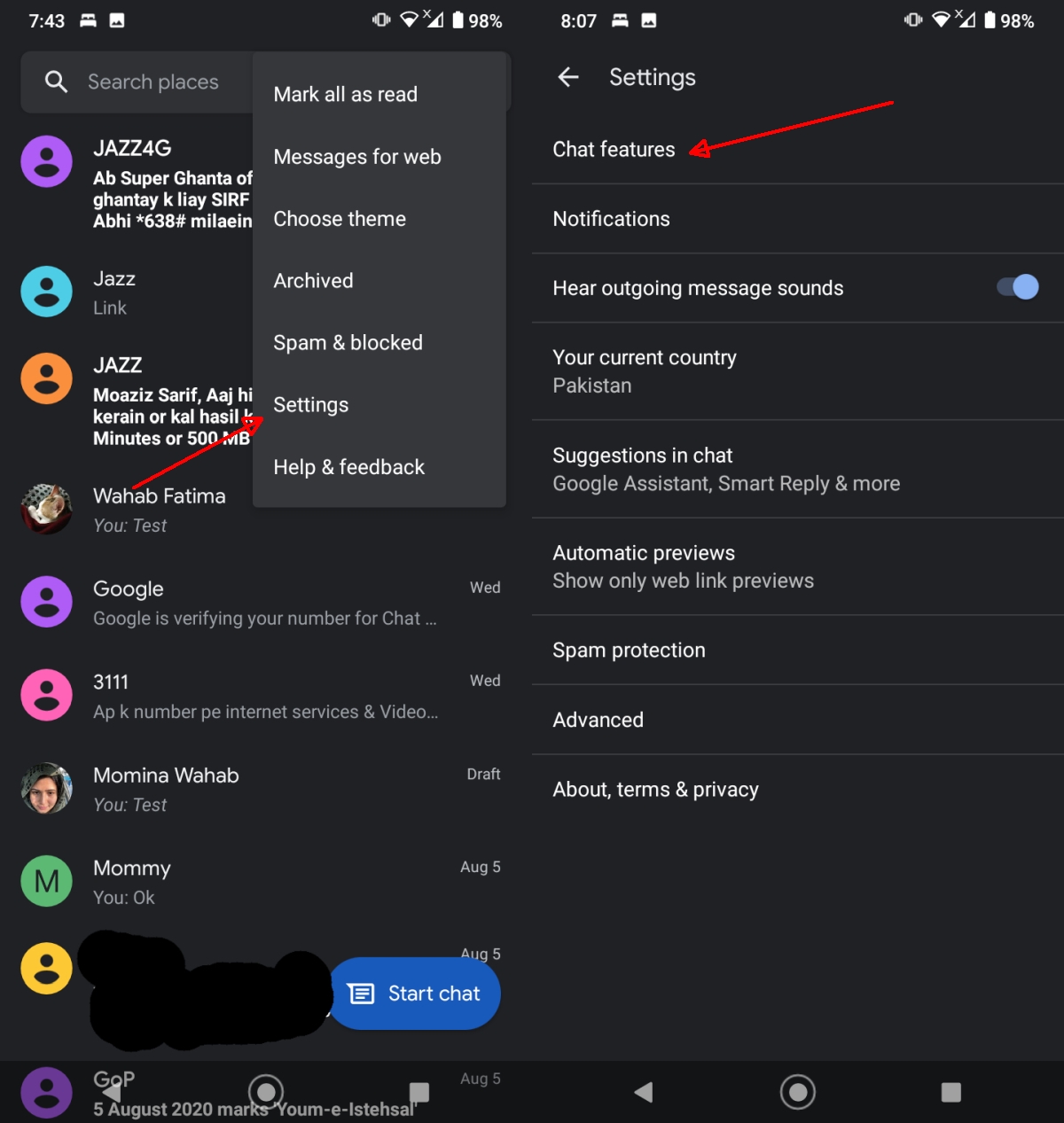
Enable Chat Features in Messages on Android
To enable Chat features in Messages on Android, you have to do the following.
- Make sure a SIM is inserted into the phone and the SIM is active.
- Make sure the Messages app is up to date.
- Open the Messages app.
- Tap the three dots button at the top and select Settings.
- Tap Chat features.
- Tap Enable.
- Tap Verify your number.
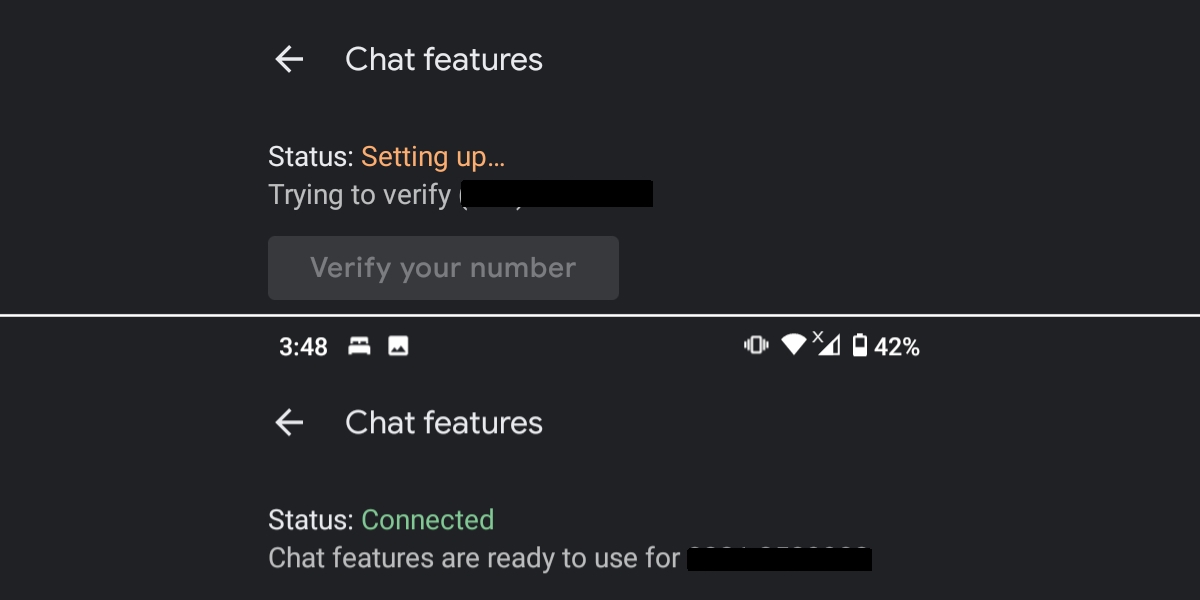
Chat features status: Setting up
Chat features take some time to enable and during that time, you will see the Status set as Setting up. Many users think the set up should be immediate, and while it should not take more than a few hours, it often ends up taking several hours or even a few days.
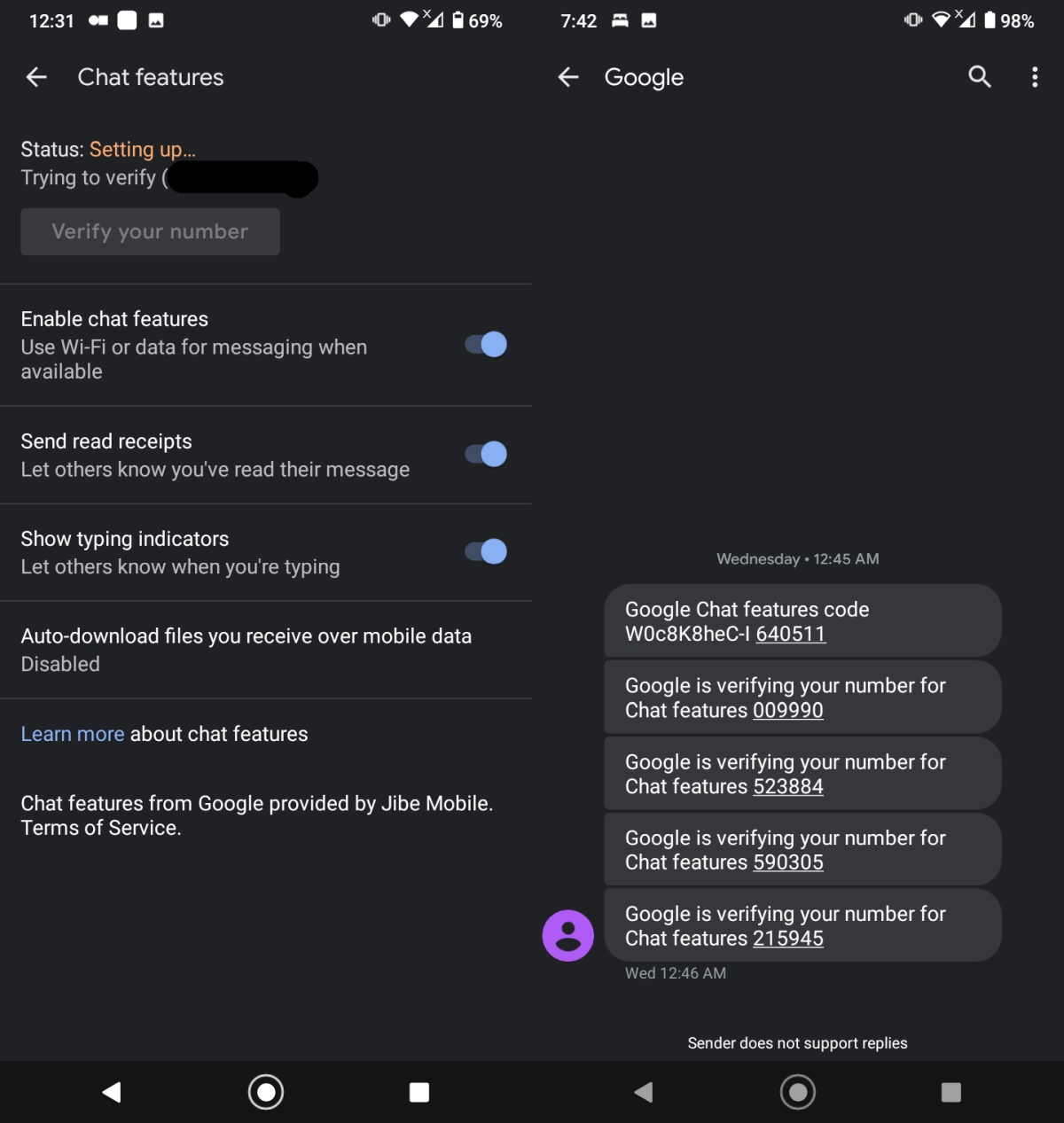
Before you try to fix the problem, check if you actually need to fix it by following these steps.
- Enable Chat features in Messages (see previous section).
- Tap Verify your number.
- Return to the Messages app.
- Look for a message from Google with a verification code.
If you’ve received the code, you only have to wait and the status will change from Setting up to Connected. Keep your phone on during this time. Wait at least 24 hours for the features to activate.
Fix Chat features status: Setting up
If you never received a message from Google, you have good reason to suspect that there is a problem enabling Chat features on your device. To fix it, try the following.
1. Restart the phone
Restarting the phone will often trigger the Chat features to start working. The status won’t change immediately but you should get those messages from Google.
- Turn your Android phone off.
- Turn it back on.
- Enable Chat features again.
- Check to see if you’ve received the verification code.
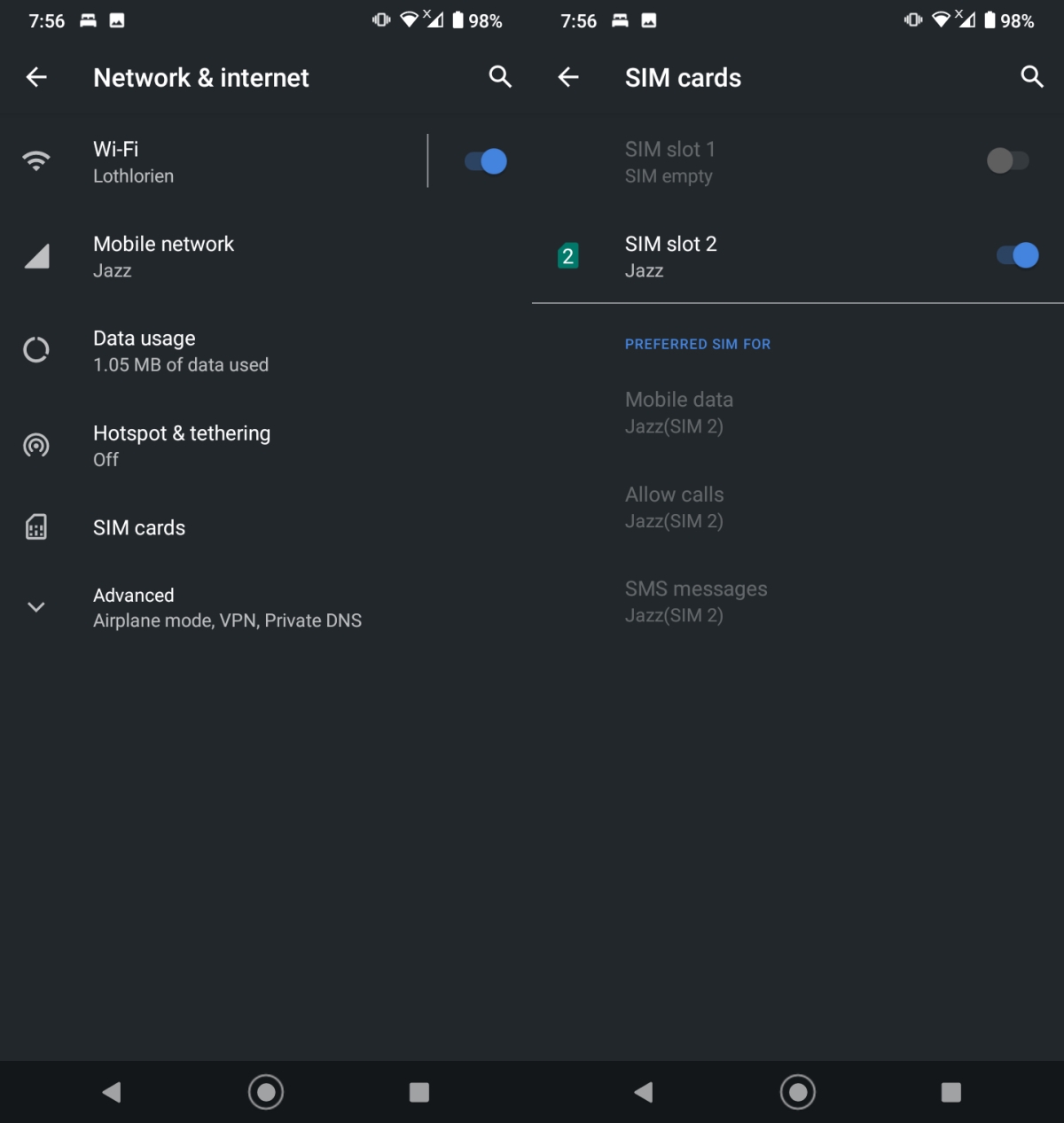
2. Check call and message preference for SIM
This fix generally applies to Android devices with a dual SIM slot but there is no harm in checking these settings on your phone even if it only has a single SIM slot.
- Open the Settings app.
- Go to Network & internet.
- Tap SIM cards.
- Make sure your SIM is enabled for Calls and Messages.
3. Change default messaging app
Changing the default messaging app can help trigger the Chat features to being the set up process. For this, we recommend installing Facebook’s Messenger app. You won’t have to use it.
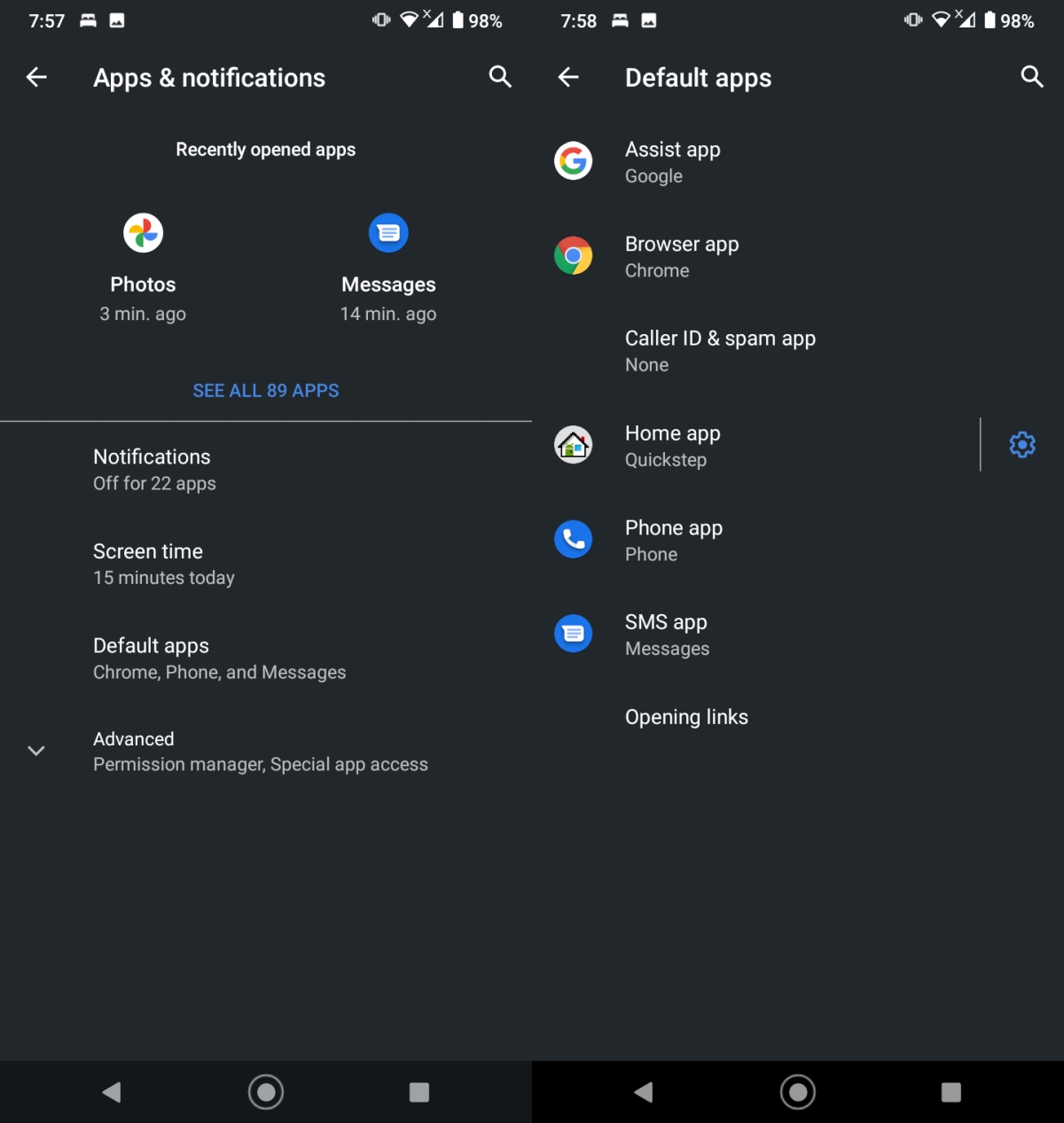
- Open the Settings app.
- Go to Apps & notifications.
- Select Default apps.
- Tap SMS app.
- Select Facebook Messenger.
- Restart the phone.
- Repeat steps 1-4.
- Select the stock Messages app.
- Activate Chat features.
4. Clear Carrier Services storage
Sometimes the reason Chat features are stuck at Setting up has to do with carrier services which are needed to verify your phone number.
- Open the Settings app.
- Go to Apps & notifications.
- Tap See all apps.
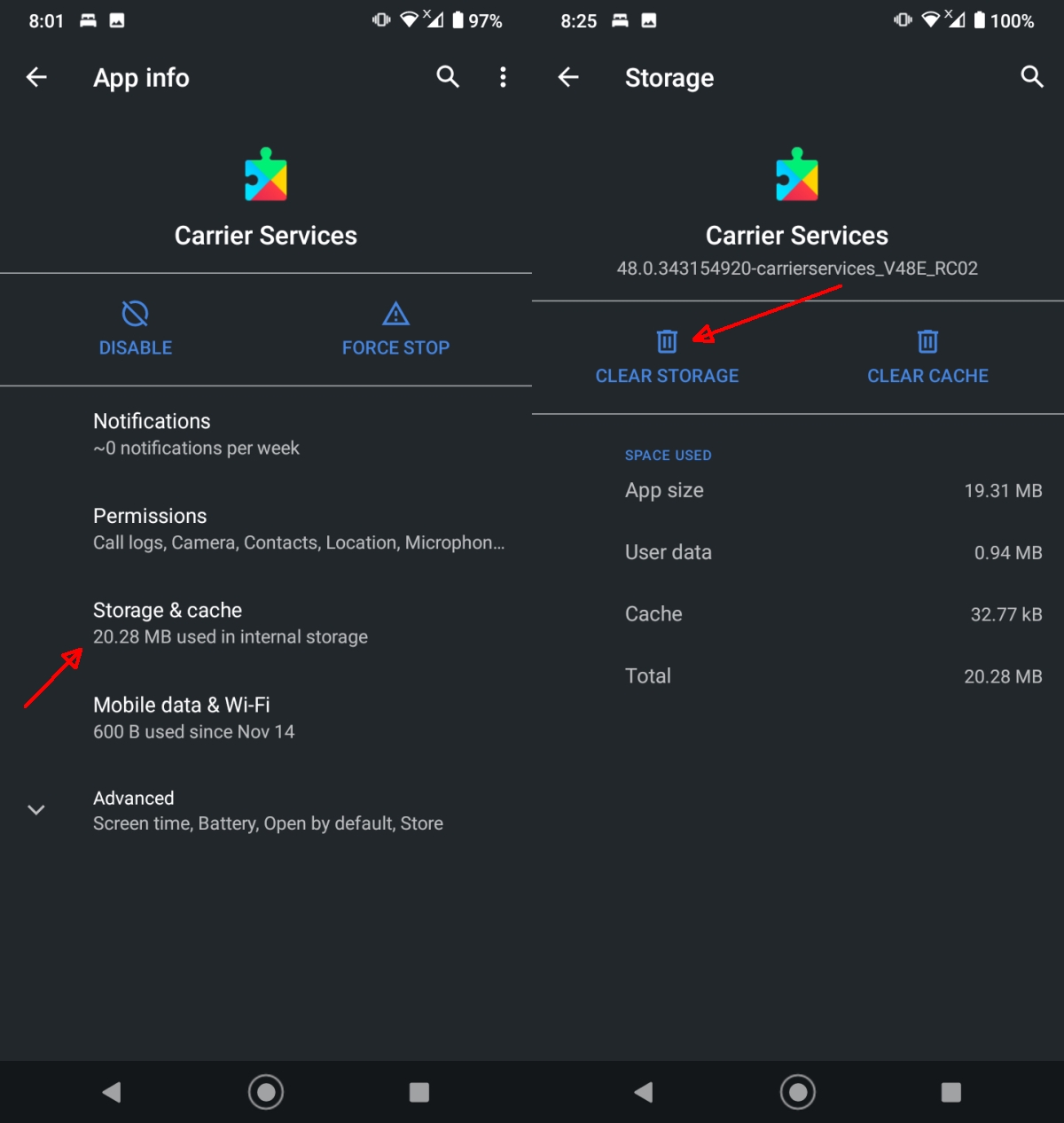
- Select Carrier Services (you might see two of them. Follow the next steps for both).
- Tap Storage & cache.
- Tap Clear Storage.
- Restart the phone.
- Enable Chat features.
Conclusion
Chat features do take some time to set up. They’ve been around for a while now but Google hasn’t managed to make the service more robust. It takes enough time for the service to activate that users suspect there’s something wrong. The tell-tale sign if the activation is actually in progress is really the Google verification code. Once you’ve received it, you’re on your way to enabling the features.





