Do you have a USB flash drive, USB SD card reader, or USB external hard drive? Want to mount your USB in Ubuntu Linux but can’t figure it out? We can help! Follow along with this guide as we show you how to mount USB devices in Ubuntu Linux!
How to mount USB in Ubuntu Linux – Ubuntu file manager
if you’re trying to mount a USB flash drive, USB hard drive, or other USB storage device on your Ubuntu Linux PC, the best way to go about it is with the Ubuntu file manager (AKA the Gnome Shell desktop file manager).
To start, you’ll need to open up the Ubuntu file manager. To open up the file manager, press the Win key on the keyboard with the mouse. After pressing the Win key with your keyboard, a search box will appear.
In the search box, type out “Files.” You can also type out “Nautilus.” When you’ve typed out the search term, a program called “Files” will appear. Click on the app icon to open it up. Alternatively, click on the file manager icon in the Ubuntu desktop dock.
Once the Ubuntu file manager is open, plug your USB device into the USB port. When you plug the device into the USB port, the Ubuntu file manager may automatically mount it.
If your Ubuntu file manager automatically mounts your USB device, you will see it on the sidebar. For example, if we plug in a 16 GB flash drive with the label “16 GB Volume” and it auto-mounts in the file manager, you will see “16 GB Volume” mounted on the side.
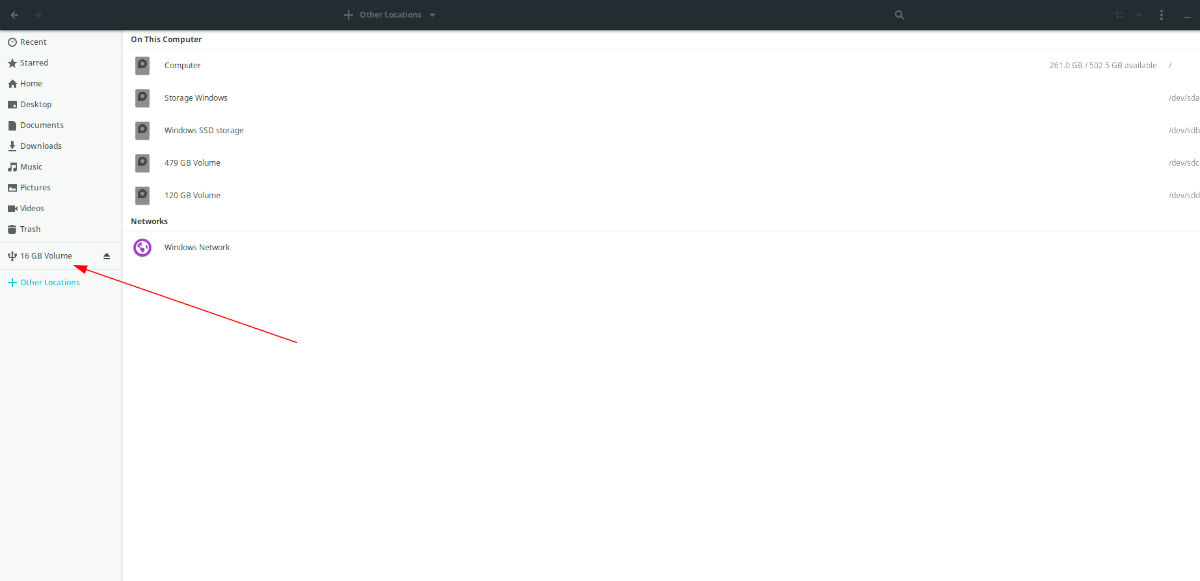
If your Ubuntu file manager doesn’t automatically mount your USB device, do the following. First, find the “Other Locations” button in the Ubuntu file manager and select it with the mouse.
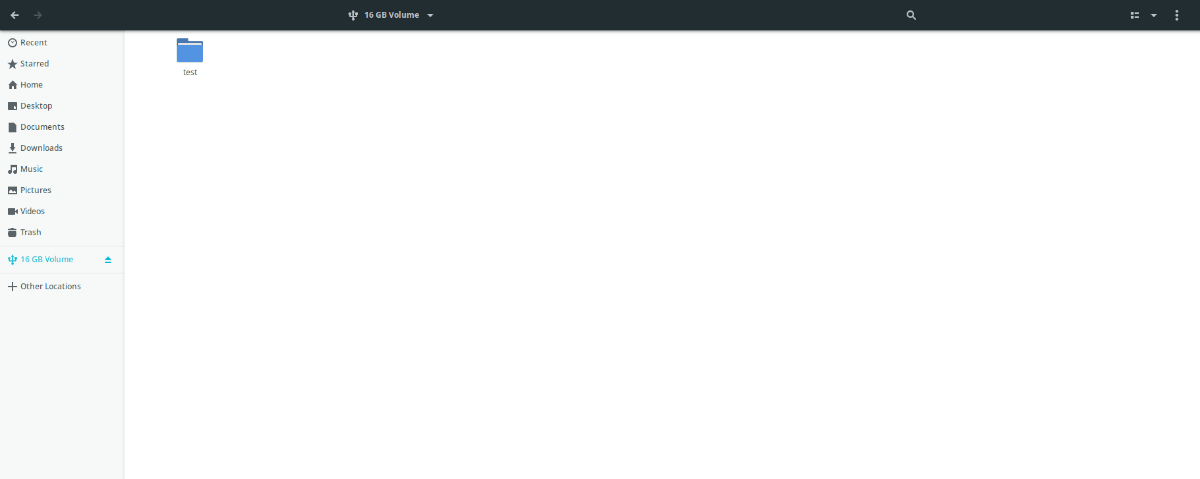
After clicking on the “Other Locations” button, the Ubuntu file manager will reveal different devices attached to your Linux PC you can mount. Select your USB device with the mouse and click on it to mount it.
How to mount USB in Ubuntu Linux – Gnome Disk Utility
While the Ubuntu file manager is very user-friendly and a great way to mount USB devices on Ubuntu Linux, it isn’t the only GUI way to do it. If you’re looking for a way to mount USB devices without dealing with the file manager but still want a GUI, you can use Gnome Disk Utility.
To start, you will need to install Gnome Disk Utility on your Ubuntu Linux PC if you do not have it installed already. The reason? Gnome Disk Utility doesn’t come pre-installed on every Ubuntu Linux spin. If you use Xubuntu, Kubuntu, Ubuntu Budgie, and others, you will need to install.
To install the Gnome Disk Utility application, open up a terminal window. Once the terminal window is open on the desktop, use the following command below to get the app installed.
Note: if you do not want to install the Gnome Disk Utility application via the terminal, you can find it in the Ubuntu Software app. Search for “Disks” via the search function, and click on the “Install” button to get it working.
sudo apt install gnome-disk-utility
With the Gnome Disk Utility application installed, launch it by searching for “Disks” in your app menu. When the app is open, plug in your USB flash drive, USB hard drive, or other USB storage device into the USB port on your Linux PC.
Gnome Disk Utility should automatically detect it and display it on the left-hand sidebar in the app after plugging in your USB device. Look for your USB flash drive in the left-hand sidebar and click on it with the mouse.
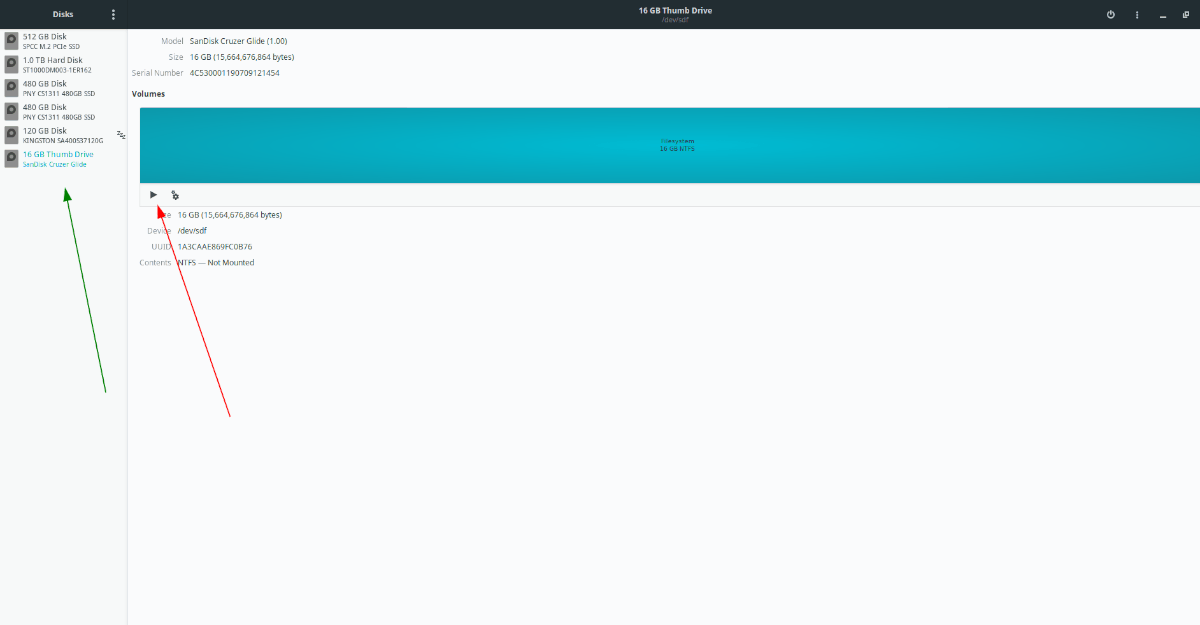
Once you’ve selected your USB device in Gnome Disk Utility, you will see an overview of the USB device’s partitions. Select the partition you wish to mount. Then, click on the “Mount” button.
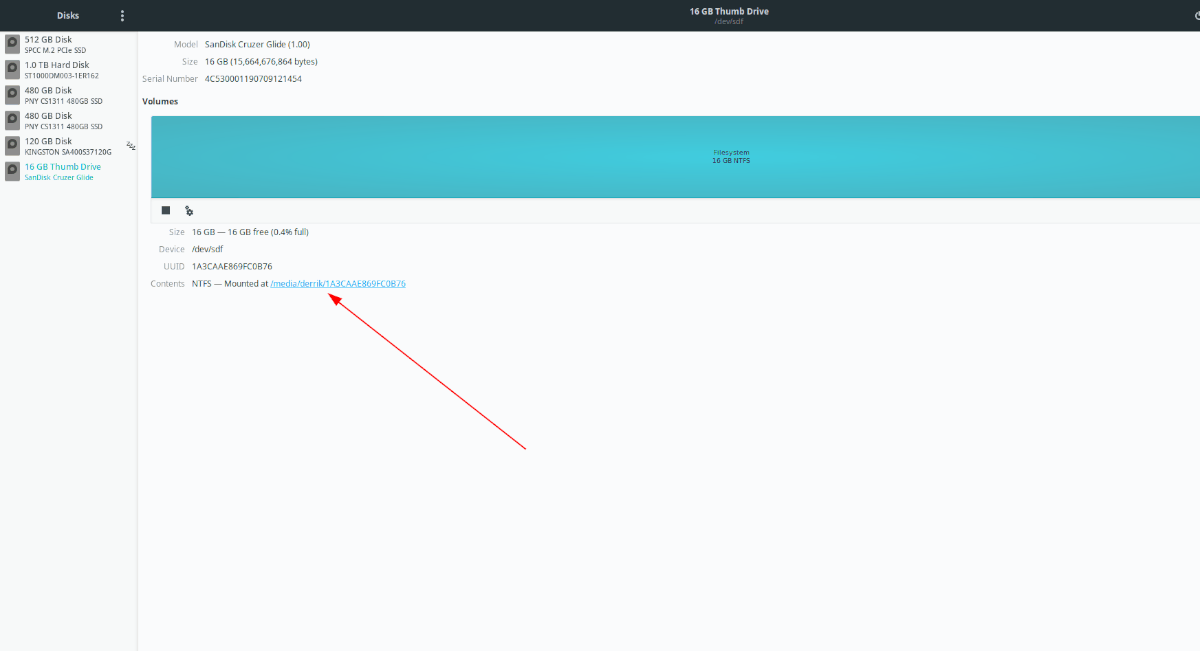
By selecting the “Mount” button, Gnome Disk Utility will mount your USB device and make it accessible via the terminal or the Ubuntu file manager. It’ll tell you where the device is mounted in the “Contents” section.
How to mount USB in Ubuntu Linux – Terminal command-line
If the Ubuntu file manager and Gnome Disk Utility don’t do it for you, you can also mount a USB device from the terminal. Here’s how to do it. To start, open up a terminal window by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T.
Once the terminal window is open and ready to go, plug in your USB flash drive to the USB port. Then, run the lsblk command.
lsblk
The lsblk command outputs every storage device connected to your Linux system. Look through the list for your flash drive and find its label.
Note: Can’t find your flash drive? Look in the size column for the size that matches your USB device. That will help you find your device.
Once you’ve found your device in lsblk, mount it in the /mnt folder using the command below. In this example, our USB device is /dev/sde. Your device label will differ. Please change /dev/sde to match your device label.
sudo mount /dev/sde /mnt





